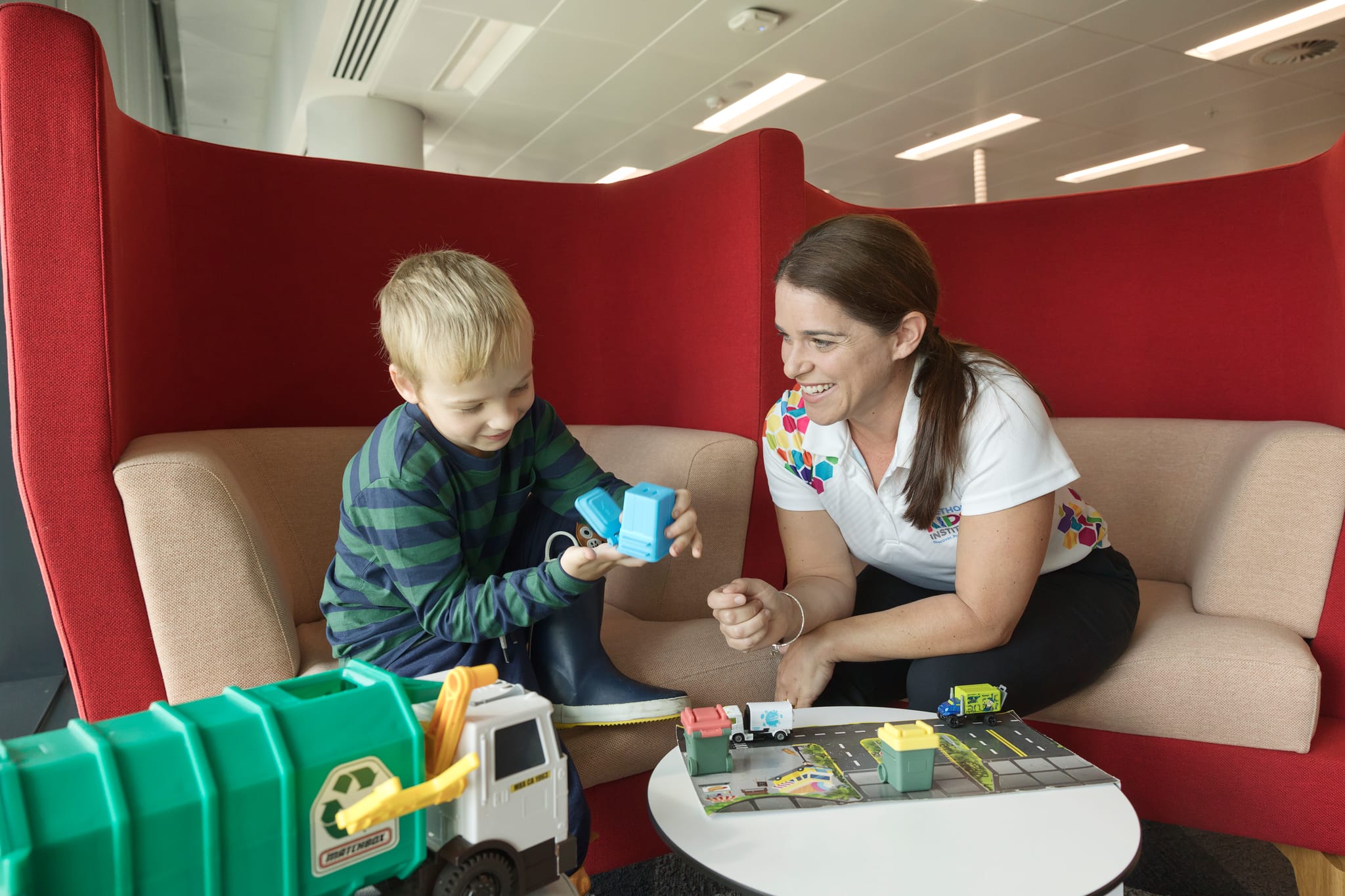
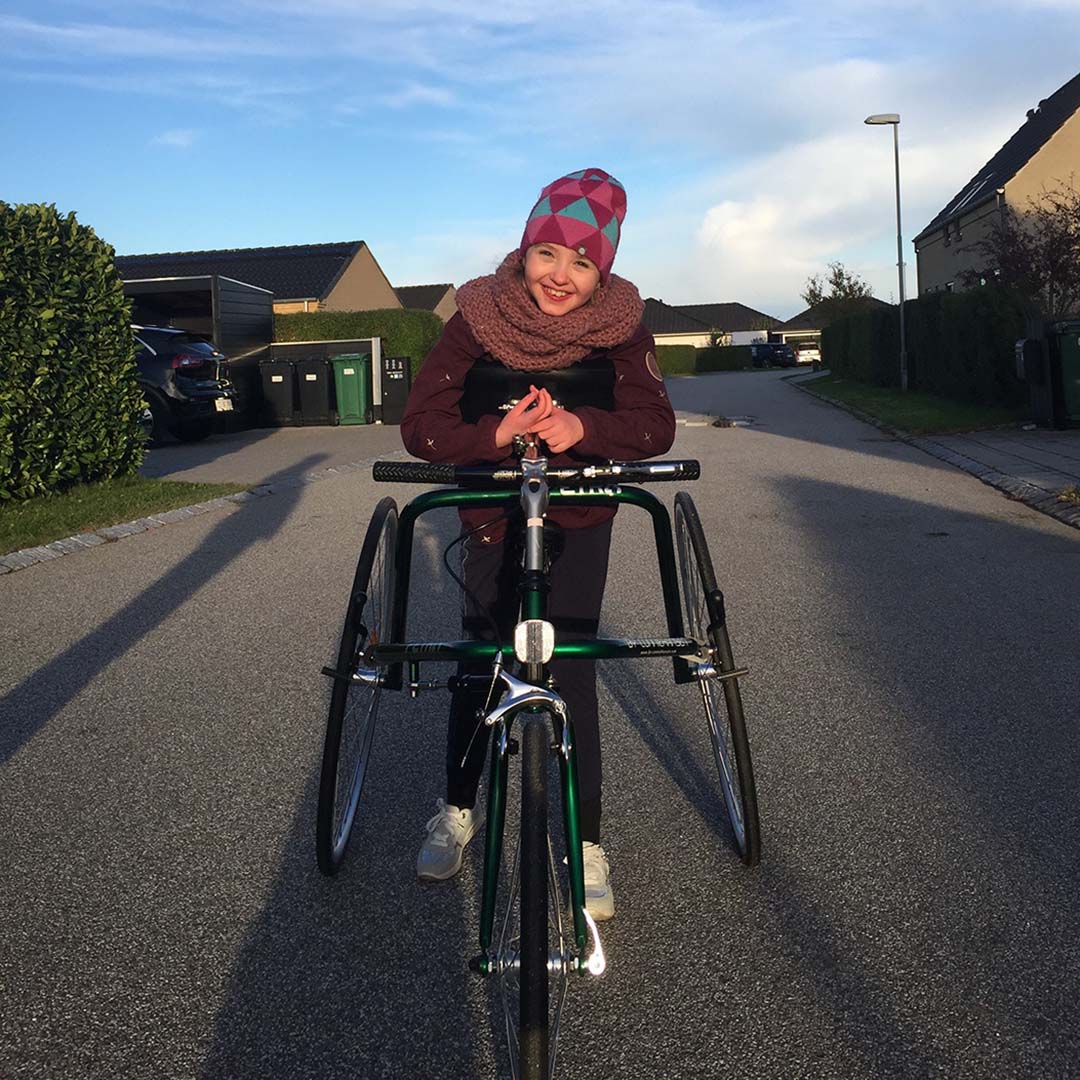
Around 1 in 10 children have a disability that impacts on their ability to function in the same way as other children.
Sometimes they are born with these disabilities, sometimes they develop after birth, and sometimes they are caused by illness or injury. There are many types of disability, including intellectual, neurological, physical, sensory, and psychological, which can influence how the child thinks, behaves, and develops skills.
Disabilities can create many barriers for children and their families, which can significantly alter their quality of life.
Our vision is that all children impacted by disability and their families will live their best lives. We will support this vision by conducting an evidence- and consumer-informed program of research, underpinned by excellence in study design, analysis, and reporting.
To achieve this vision, we will:
- Engage with children with disability and their families across all walks of life to better understand their needs,
- Prevent or reduce disability and ensure that our research helps support meaningful and impactful changes,
- Engage key stakeholders to improve access to services and influence policy and practice.
- Collaborate with the community, health professionals, service providers, researchers, and policy makers.
Team leader

BApplSci (physio) MSc PhD
Team members (17)

MBChB MPH

BPsych BSc (Hons) PhD
Senior Research Fellow

PhD
Senior Research Officer

BSc (Hons), PhD
Senior Research Officer, Child Disability

B Psych (First Class Honours), PhD (Psychology)
Senior Research Officer

PhD
Senior Research Fellow

BPsych(Hons), PhD (Psychology)
Research Officer

BA (Hons) MSc
Biostatistician

MBChB., DipRACOG., Cert.HPRT, FRACP., PhD

BE MPH
Research Officer

B. App Sci (Physio.)
Research Officer

BPsych, PhD

BDS, MDS, MFDS RCPS (Glasg.), DDPH RCS (Eng)

MBBS, MPH, MMedStat
Research Officer

BPsych MPH PhD Candidate

BSc(Hons)
PhD Candidate
Featured projects
Using ambulatory monitoring to investigate awake breathing irregularities in Rett syndrome in Australian population-based and Italian clinic samples
Towards evidence based care for Rett syndrome: a research model to inform management of rare disorders
Other projects
THINK BIG - Neurodevelopmental Disorders The natural history of the MECP2 Duplication disorder: Australian surveillance and plans for development of an international register Multi-site validation of a suite of clinical outcome measures for clinical trial readiness in the CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder Multigenerational Familial and Environmental Risk for Autism (MINERvA) Network Mothers with intellectual disability and their children in Western Australia International Rett syndrome study: InterRett All Child Disability projects