Search

News & Events
Boosting mums’ immunity could save newborns from deadly respiratory virusesPerth respiratory researchers have discovered that giving an immune booster to mothers during pregnancy could increase their newborns’ resistance to severe and life-threatening respiratory viral infections.
News & Events
Lots to celebrate as Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre turns 2As the Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre turns two, the Centre celebrates its achievements and thanks everyone involved in the work of the Centre.

News & Events
Researchers one step closer to preventing asthma in childrenWal-yan Respiratory Research Centre PhD student Niamh Troy has found how OM85 helps babies fight off severe lung infections.

News & Events
New study to find COVID-fighting properties in existing medications thanks to national grantNearly 50 existing prescription medications already used by Australians will be tested by new research in the fight against COVID’s mutant variants.
News & Events
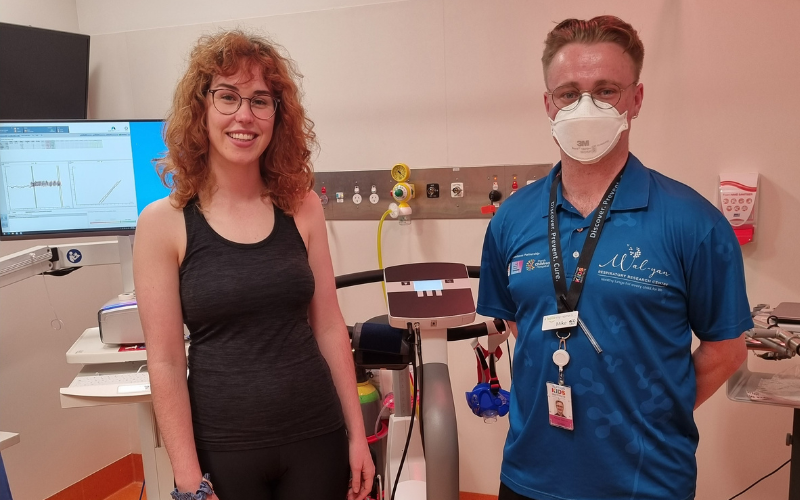
Thumbs up from first preterm study participant to use new lung function testing equipmentNatasha, who is a participant in the West Australian Lung Health in Prematurity (WALHIP) study, this week became the first person to receive a lung health assessment using new state-of-the-art lung function testing equipment at Perth Children’s Hospital.
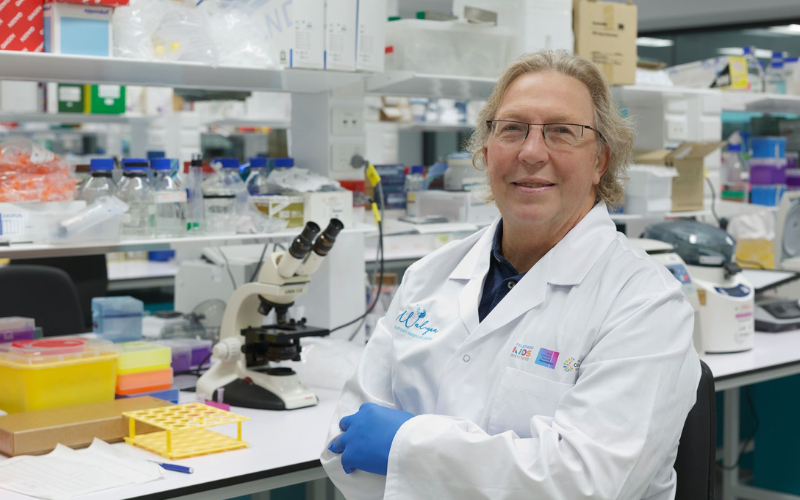

News & Events
State Government grant to support development of new therapies for respiratory virusesA project to be undertaken by a team of researchers at the Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre, led by chief investigator Professor Stephen Stick, aims to develop interventions that could provide protection in the event of a new pandemic, and against common viruses already infecting children in WA.
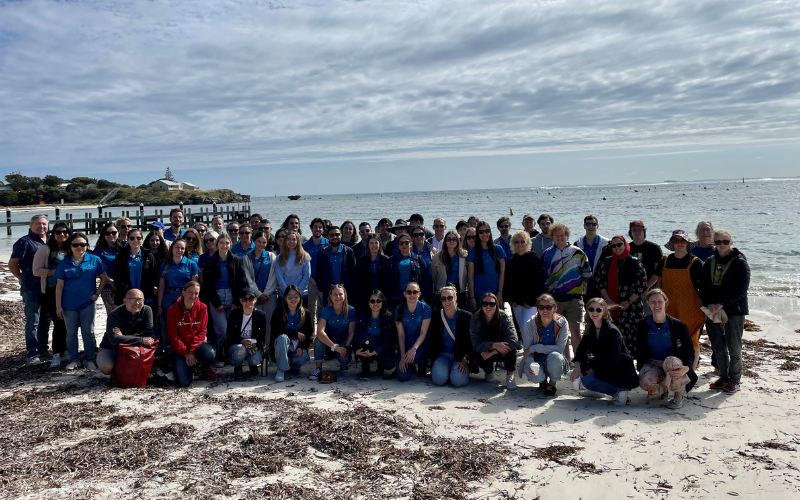

News & Events
Great minds come together at Wal-yan Scientific RetreatWal-yan Respiratory Research Centre team members and special guests travelled to Wadjemup (Rottnest) on 27 and 28 October to spend an intensive two days together learning about, and providing input into, the broad range of research projects underway within the Centre.
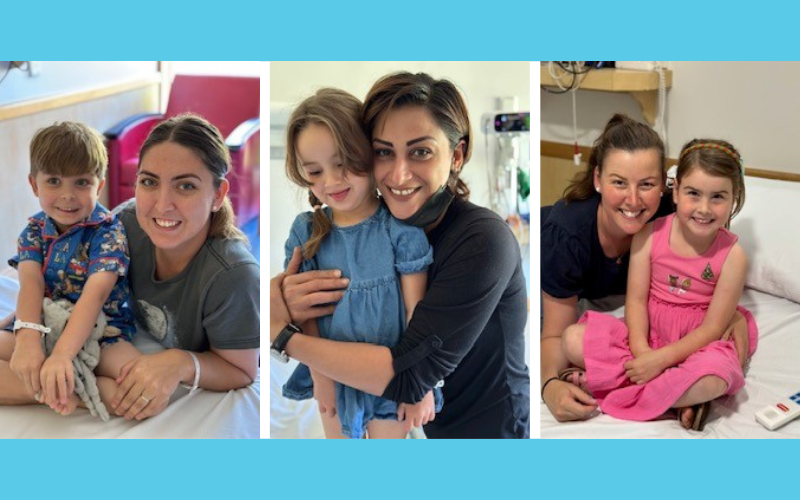

News & Events
300th participant recruited to crucial respiratory research programA research program, which enables over 25 important respiratory research studies to be undertaken, celebrated the recruitment of its 300th participant on 14 December 2022.

News & Events
Seven innovative lung health research projects supported by Wal-yan Centre fundingSeven innovative lung health research projects have received funding support as the 2023 Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre Strategic Inspiration Projects.

News & Events
Wal-yan researchers welcomed at scientific meeting in New ZealandMore than 14 researchers from the Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre will be welcomed as presenters and facilitators at The Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and The Australia and New Zealand Society of Respiratory Science (TSANZSRS) Annual Scientific Meeting (ASM) this weekend.
